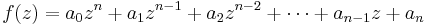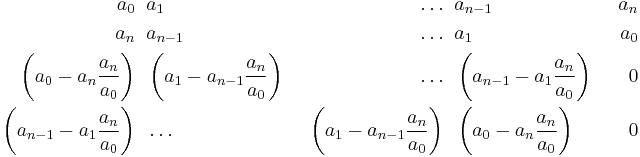Jury stability criterion
The Jury stability criterion is a method of determining the stability of a linear discrete time system by analysis of the coefficients of its characteristic polynomial. It is the discrete time analogue of the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion. The Jury stability criterion requires that the system poles are located inside the unit circle centered at the origin, while the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion requires that the poles are in the left half of the complex plane. The Jury criterion is named after Eliahu Ibraham Jury.
Method
If the characteristic polynomial of the system is given by
then the table is constructed as follows:
That is, the first row is constructed of the polynomial coefficients in order, and the second row is the first row in reverse order and conjugated.
The third row of the table is calculated by subtracting 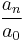 times the second row from the first row, and the fourth row is the third row with the first n elements reversed (as the final element is zero).
times the second row from the first row, and the fourth row is the third row with the first n elements reversed (as the final element is zero).
The expansion of the table is continued in this manner until a row containing only one non zero element is reached. If the first element of the first row of every row pair is positive at this point, then the system is stable.
Note the {a_n}/{a_0} is for the 1st 2 rows. Then for 3rd and 4th row the coefficient changes. This can be viewed as the new polynomial which has one less degree and then continuing. This is very easy to implement using dynamic arrays on a computer. It also tells whether all the modulus of the roots (complex and real) lie inside the unit disc. Vector v contains the real coefficients of the original polynomial in the order from highest degree to lowest degree.
/* vvd is the jury array */
vvd.push_back(v); // Store the first row
reverse(v.begin(),v.end());
vvd.push_back(v); // Store the second row
for(i=2;;i+=2)
{
v.clear();
double mult=vvd[i-2][vvd[i-2].size()-1]/vvd[i-2][0]; // This is an/a0 as mentioned in the article.
for( j=0;j<vvd[i-2].size()-1;j++) // Take the last 2 rows and compute the next row
v.push_back(vvd[i-2][j] - vvd[i-1][j]*mult);
vvd.push_back(v);
reverse(v.begin(),v.end()); // reverse the next row
vvd.push_back(v);
if(v.size()==1) break;
}
Check is done using
for(i=0;i<vvd.size();i+=2)
{
if(vvd[i][0]<=0) break;
}
if(i==vvd.size())
"All roots lie inside unit disc "
else
"no"
References
For more details please check these references:
For advanced resources:
- http://users.rsise.anu.edu.au/~briandoa/pubs/R300AN499.pdf (Archive.org version: http://web.archive.org/web/20080802013128/http://users.rsise.anu.edu.au/~briandoa/pubs/R300AN499.pdf )
- http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0165168496000771
- http://www.laas.fr/~henrion/Papers/lyap.ps.gz
For implementations:
- http://www.ticalc.org/archives/files/fileinfo/426/42696.html (TI-83+/84+ graphing calculators)